
Reverse Osmosis system
Summary
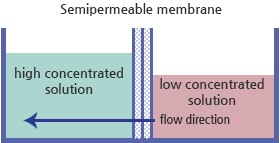
Osmosis is the spontaneous passage of a liquid from a dilute to a more concentrated solution through a semipermeable membrane, which allows passage of the liquid but not of dissolved solids. This phenomenon shows how plants absorb water and how living cells can gain energy by endocytosis process.
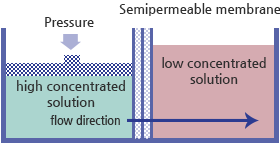
Reverse osmosis (RO) is the forced reversal of this natural phenomenon, usually accomplished by applying enough pressure to the concentrated solution to overcome the natural pressure or osmotic pressure of the less concentrated solution. In this process, 96% of minerals, 90% of dissolved solids, and 99% of bio-organism and chloride material can be removed.
Pictures below explain how both osmosis and reverse osmosis system work.
Osmosis
Reverse osmosis
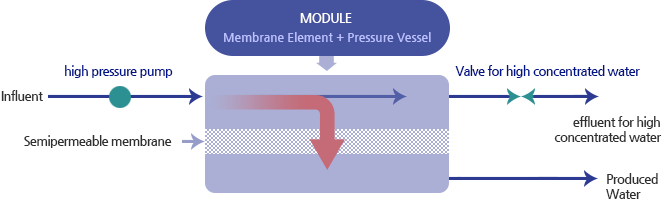
Reverse Osmosis System Process
Summary
Reverse osmosis system is processed horizontally. By pressing influent, incoming water is separated into produced water and high concentrated water. A valve on the semipermeable membrane controls flow, and it also can manage the flow rate. In this process, treated water can be drained.
The equations for RO system are:
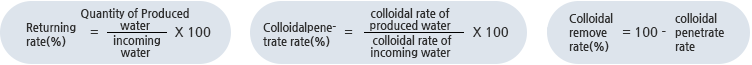
RO system is used for
- Pretreatment for ultra-pure water treatment system
- Backwash or supplemental water for low ionized or organic water treatment system for semiconductor industry and pharmaceutical industry.
Reverse Osmosis System Process
Benefits
- Removal of Salt: blocks most of salt but water can pass through the membrane.
- Elimination of particular substance (Organic, Inorganic, Microorganism)
- Cost reduction by treating water without changing phase.
Applications
- Drinking water
- Desalination
- Industrial wastewater
- Hemodialysis unit
- Pharmaceutical water
- Beverage Industry


